Customer Driven Marketing
- Nature of marketing
- Marketing: The function of business
- Positioning
- Case Study: Marriott
- Case study: Apple
- Developing a marketing strategy
Nature of marketing
Marketing is…
A group of activities designed to expedite transactions by creating, distributing, pricing, and promoting goods, services, and ideas.
- Marketing activities create value
- Important part of a firm’s overall strategy.
Marketing is not…
- Manipulating consumers to get them to buy products they don’t want
- Just advertising and selling
The exchange relationship
- Each participant must be willing to give up “something of value” to receive “something” held by the other.
- The tangible product itself may not be as important as the image of the benefits associated with the product
- Capability gained from using a product
- Image evoked by a product
- Brand name
Functions of Marketing
- Buying
- Selling
- Transportation
- Storing
- Grading
- Financing
- Marketing research
- Risk taking
Creating value with Marketing
- Value is a customer’s subjective assessment of benefits relative to costs in determining the worth of a product
- Customer value = customer benefits - customer costs
- Benefits are anything a buyer receives in exchange.
- Costs are anything a buyer gives up to obtain a product’s benefits.
The marketing concept
- Ideat that an organization should try to satisfy customers’ needs through coordinated activities that also allow it to achieve its own goals.
- Businesses must:
- Find out what customers desire
- Develop the good, service, or idea to satisfy that want
- Get the product to the customer
- Continually alter, adapt, and add products to keep pace with changing customer demands.
Marketing: The function of business
Marketing and innovation are the two chief functions of business. You get paid for creating a customer, which is marketing. And yuo get paid for creating a new dimension of perfomance.
Push - pull theory
Product
The combination of your company, what your competitors can provide, and what the customers are requiring. Once any of the factors change, the product will have to change as well.
The positioning of a product is positioning = differentiation + segmentation. How is our product differentiated from the competition?
Pricing models
- Cost-based
- Value-based
- Competition-based
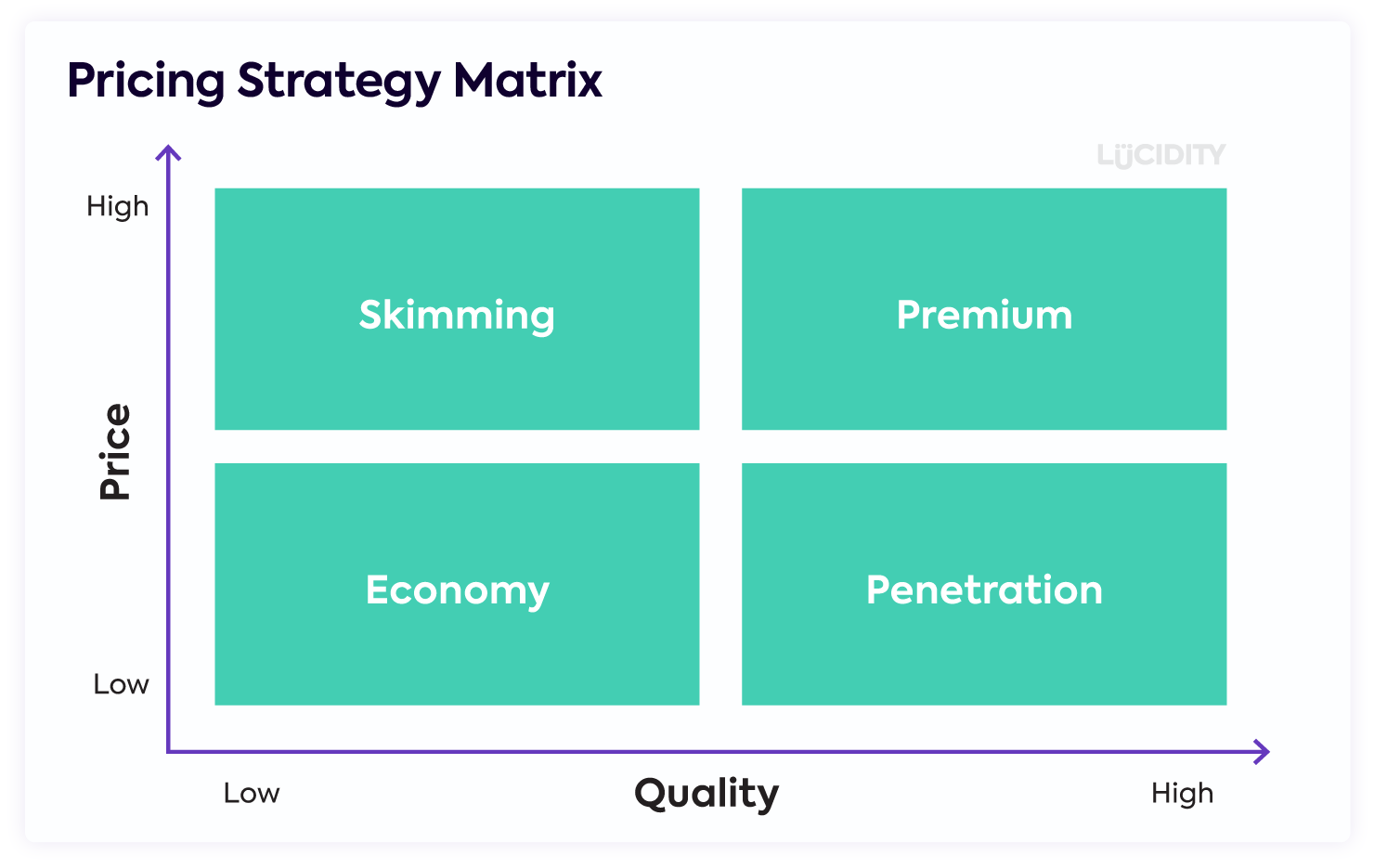
Positioning
Positioning refers to the place that a brand occupies in the minds of the customers and how it is distinguished from the products of the competition.
What is your uniqueness?
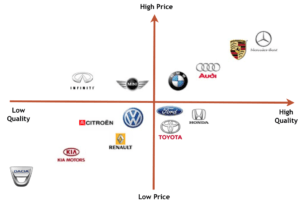
- Determine company uniqueness by comparing to competitors
- Identify current market position
- Competitor positioning analysis
- Develop a positioning strategy
Case Study: Marriott
- Intuitive website for brand education
- Segments market by demographics and psychographics
- Serves same psychographic group over different pricepoints
- Always be where your customer is
Critical Thinking Questions
What are some ways that Marriott uses market research to discover what customers want?
They seperate their customers based on Psychographics and determine what they are looking for in a hotel
- Price points
- High price, high service
- High price, self service but more convinient
- Low price, self service
- Type of hotel
- Destination/unique
- Cookie-cutter (i.e. airport hotels)
- Level of service
- Bellman/concierge/room service
- Acccessability of destination
- Does a customer plan to leave the hotel during the trip or does the hotel internalize everything
They need to find where their target customers are located (print media, social media, social influencers, online, etc).
They also conduct market research to decide what brand of hotel to build and service at a given location.
- Airports have simple, cookie cutter hotels
- Destinations often have unique cultural hotels/resorts
Case study: Apple
Spent 1.8 billion on marketing, developers who make the product pages earn 800,000/year and animators make 600k. Spent 500 million marketing Apple TV in the last year.
- Establish themselves as a premium brand
- Very good with audience insights
- Good at selling customers on products they don’t necessarily use
- Create a product and a need before it exists (3 steps ahead of the comsumer)
- Creates fomo
- Vertically integrated
- Planned obsolescence
- Stores and displays are very appealing
Developing a marketing strategy
- Making products availible to customer in the quantities desired
Promotion
- Persuasive form of communication that attempts to expedite a marketing exchange by influencing individuals, groups, and organizations to accept goods, services, and ideals.
- Includes advertising, personal selling, publicity, and sales promotion
- Digital advertising on websites and social media sites are growing.
USP = Unique Selling Proposition
- Primary Data
- Observed, recorded, or collected directly from respondents
- “Mystery shoppers”, surveys, and focus groups
- Ethnographic or observational research
- Secondary data
- Compiled inside or outside an organization for some purpose other than chanaging the current situation
- Compiled by the U.S. Census Bureau and other government agencies, databases created by marketing research firms.
Online marketing research
- Marketing research of the future
- Virtual testing
- Digital and social media sites
- Online surveys
- Marketing analytics
Product strategy
Product line is the group of closely related products that are treated as a unit